| [1]Wright KT, Masri W, Osman A,et al.Concise Review: Bone Marrow for the Treatment of Spinal Cord Injury: Mechanisms and Clinical Applications.J Stem Cells.2011; 29(2):169-178.[2]Huang Y,Jia X,Bai K,et al.Effect of fluid shear stress on cardiomyogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. J Arch Med Res.2010;41(7):497- 505.[3]Woodbury D, Schwarz EJ, Prockop DJ,et al.Adult rat and human bone marrow stromal cells differentiate into neurons.J Neurosci Res.2000;61:364-370.[4]Radtke C, Schmitz B, Spies M, et al.Peripheral glial cell differentiation from neurospheres derived from adipose mesenchymal stem cells.Int J Devl Neuroscience.2009; 27(8):817-823.[5]Wislet-Gendebien S, Laudet E, Neirinckx V,et al.Adult Bone Marrow: Which Stem Cells for Cellular Therapy Protocols in Neurodegenerative Disorders? J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012; 2012:601560.[6]Mrówczyński W, Celichowski J, Krutki P,et al.Changes of the force-frequency relationship in the rat medial gastrocnemius muscle after total transection and hemisection of the spinal cord. J Neurophysiol.2011;105(6):2943-2950.[7]Hofstetter CP, Sehwarz EJ, Hess D,et al. Marrow stromal cells from guiding strands in the injured spinal cord and promote recovery.Proc Nad Aead Sei USA.2002;99(4):2199- 2204.[8]Ankeny DP, McTique DM, Jakeman LB,et al.Bone marrow transplants provide tissue protection and directional guidance for axon after contusive spinal cord injury in rats.J Exp Neurol. 2004;190(1):17-31.[9]Scheff SW, Saucier DA, Cain ME. A statistical method for analyzing rating scale data: the BBB locomotor score.J Neurotrauma.2002;19(10):1251-1260.[10]Mafi P, Hindocha S, Mafi R,et al.Adult Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Cell Surface Characterization - A Systematic Review of the Literature.J Open ORTHOP J. 2011; 5(Suppl 2): 253-260.[11]Basso DM, Beattie MS and Bresnahan JC.A sensitive and reliable locomotor rating scale for open field testing in rats.J Neurotrauma.1995;12(1):1-21.[12]Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC,et al.Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells.J Science. 1999;284(5411):143-147.[13]Arinzeh TL. Mesenchymal stem cells for bone repair: preclinical studies and potential orthopedic applications.J Foot Ankle Clin.2005;10(4):651-665.[14]Caplan AI. Adult mesenchymal stem cells for tissue engineering versus regenerative medicine. J Cell Physiol. 2007;213(2):341-347.[15]Barry FP, Murphy JM.Mesenchymal stem cells: clinical applications and biological characterization.J Int J Biochem Cell Biol.2004;36(4):568-584.[16]Helder MN, Knippenberg M, Klein-Nulend J,et al.Stem cells from adipose tissue allow challenging new concepts for regenerative medicine. Tissue Engineering.2007;13(8): 1799-1808.[17]Trubiani O, Orsini G, Caputi S,et al.Adult mesenchymal stem cells in dental research: a new approach for tissue engineering.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol.2006;19(3):451- 460.[18]Kopen GC, Prockop DJ, Phinney DG.Marrow stromal cells migrate throughout forebrain and cerebellum, and they differentiate into astrocytes after injection into neonatal mouse brains.J Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.1999;96(19):10711-10716.[19]Abouelfetouh A, Kondoh T, Ehara K,et al.Morphological differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells into neuron-like cells after co-culture with hippocampal slice.J Brain Res. 2004; 1029(1):114-119.[20]Jin K, Mao XO, Batteur S,et al.Induction of neuronal markers in bone marrow cells: differential effects of growth factors and patterns of intracellular expression. Exp Neurol.2003;1841: 78-89.[21]Zhou J, Tian GP, Wang JE, et al. In vitro differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells and bone marrow-derived stromal stem cells into neuronal-like cells. Neural Regen Res. 2011; 6(19):1467-1472.[22]Li Q, Geng YJ, Lu L, et al. Platelet-rich fibrin-induced bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell differentiation into osteoblast-like cells and neural cells. Neural Regen Res. 2011;6(31):2419-2423.[23]Neuhuber B, Himes BT, Shumsky JS,et al.Axon growth and recovery of function supported by human bone marrow stromal cells in the injured spinal cord exhibit donor variations. J Brain Res.2005;1035:73-85.[24]Crigler L, Robey RC, Asawachaicharn A,et al. Human mesenchymal stem cell subpopulations express a variety of neuro-regulatory molecules and promote neuronal cell survival and neuritogenesis. Exp Neurol. 2006;198:54-64.[25]Poll D, Parekkadan B, Borel Rinkes IHM,et al.Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Protection and Repair of Injured Vital Organs. Cellular and Molecular Bioengineering.2008;1:42-50.[26]Uccelli A, Benvenuto F, Laroni A,et al.Neuroprotective features of mesenchymal stem cells.J Best Pract Res Clin Haematol.2011;24:59-64.[27]da Silva Meirelles L, Fontes AM, Covas DT,et al.Mechanisms involved in the therapeutic properties of mesenchymal stem cells.J Cytokine Growth Factor Rev.2009;20:419-427.[28]Caplan AI, Dennis JE.Mesenchymal stem cells as trophic mediators. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry. 2006;98:1076- 1084.[29]Wu S, Suzuki Y, Ejiri Y,et al.Bone marrow stromal cells enhance differentiation of co-cultured neurosphere cells and promote regeneration of the injured spinal cord.J Neurosci Res. 2003;72:343-351.[30]Barnabé GF, Schwindt TT, Calcagnotto ME,et al. Chemically- Induced RAT Mesenchymal Stem Cells Adopt Molecular Properties of Neuronal-Like Cells but Do Not Have Basic Neuronal Functional Properties.PLoS ONE.2009;4(4): e5222.[31]Tarasenko YI, Gao J, Nie L, Johnson KM,et al.Human fetal neural stem cells grafted into contusion-injured rat spinal cords improve behavior.J Neurosci Res.2007;85:47-57.[32]Cai PQ, Sun GY, Cai PS, et al. Survival of transplanted neurotrophin-3 expressing human neural stem cells and motor function in a rat model of spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2009;4(7):485-491.[33]Osaka M, Honmou O, Murakami T,et al.Intravenous administration of mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow after contusive spinal cord injury improves functional outcome.J Brain Res.2010;1343:226-235.[34]Li L, Lü G, Wang YF, et al. Glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA expression in a rat model of spinal cord injury following bone marrow stromal cell transplantation. Neural Regen Res 2008;3(10):1056-1059.[35]Li BC, Li Y, Chen LF,et al.Olfactory ensheathing cells can reduce the tissue loss but not the cavity formation in contused spinal cord of rats.J Neurol Sci.2011;303:67-74. |
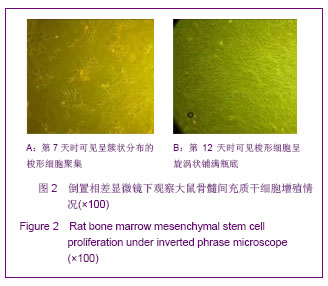
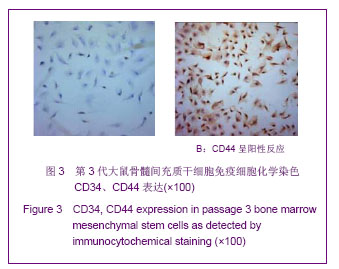
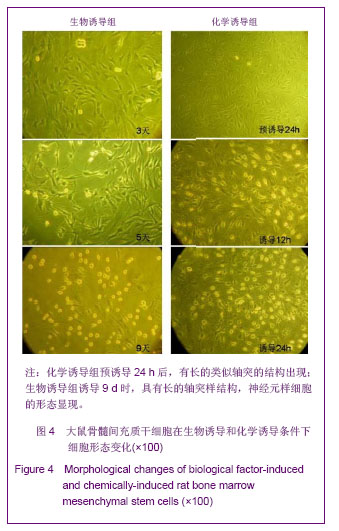
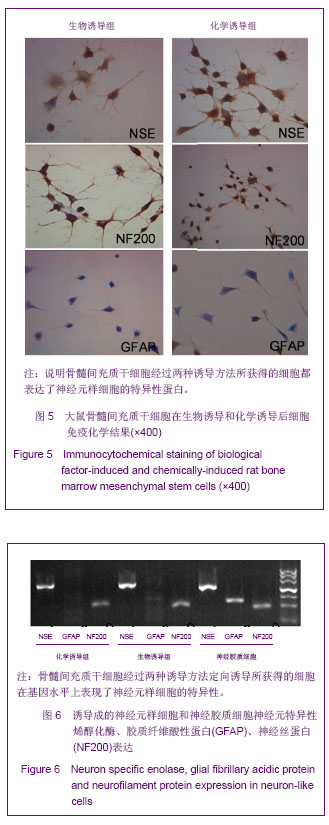
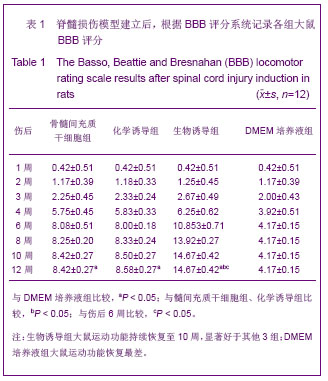
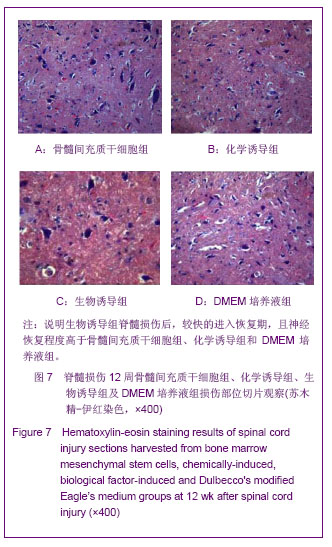
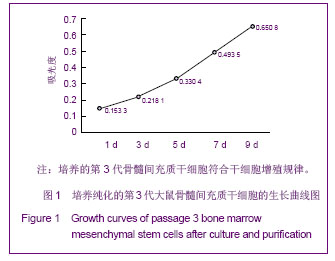
.jpg)